

Parts of speech are categories of words that perform similar grammatical roles in phrase and sentence structures. You might wonder what the different parts of speech are and how to identify them. This reference explains parts of speech, including nouns, verbs, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, determiners, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections, with examples.
You’ll also learn about open and closed word classes, how to determine a part of speech in a sentence, and their roles in simple and complex sentence constructions. This guide includes a useful picture, a video, and a quiz on parts of speech to help solidify your understanding.

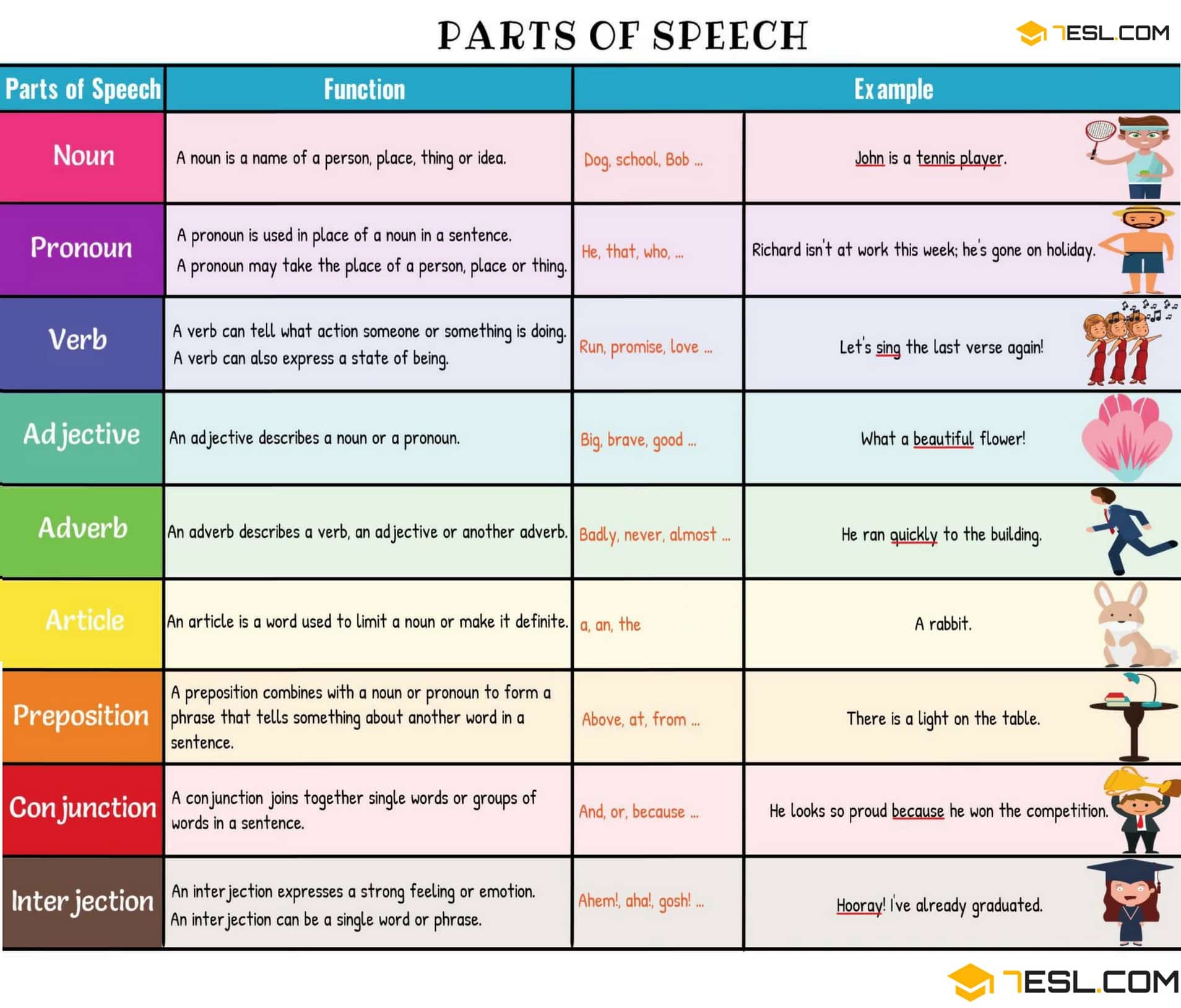
Parts of speech are word categories defined by their roles in sentence structures. These categories are organized by the functions and meanings they convey. In English, there are around ten common parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, determiners, and articles.
Closed word classes are parts of speech that do not have newer words introduced over time. These include pronouns, conjunctions, determiners, and prepositions.
Open word classes are parts of speech that can have newer words introduced over time. These include nouns, verbs, adjectives, interjections, and adverbs.
A noun gives a name to something. There are different types of nouns like proper, collective, possessive, and common nouns.
Examples:
Jeffrey, Korea, pen, New Year, dog, cat, elephant, garden, school, work, music, town, Manila, teacher, farmer, Bob, Sean, Michael, police officer, France, coffee, football, danger, happiness…
Example sentences:
Common Noun: Names a general item.
Proper Noun: Names a specific item.
Collective Noun: Refers to a group.
Possessive Noun: Shows ownership.
A verb describes an action. There are three main types: action, linking, and modal verbs.
Examples:
Walk, is, seem, realize, run, see, swim, stand, go, have, get, promise, invite, listen, sing, sit, laugh, walk…
Example sentences:
Action Verb: Describes an action.
Linking Verb: Connects the subject to a noun, adjective, or pronoun.
Modal Verb: Helps the main verb and shows the speaker’s thoughts.
A pronoun replaces a noun. There are various types of pronouns like reflexive, indefinite, possessive, and relative pronouns.
Examples:
I, me, we, you, he, she, yours, himself, its, my, that, this, those, us, who, whom
Example sentences:
Reflexive Pronoun: Refers to self.
Indefinite Pronoun: Refers to a non-specific person or item.
Possessive Pronoun: Shows ownership.
Relative Pronoun: Introduces an adjective clause.
An adjective describes a noun or pronoun.
Examples:
Beautiful, seven, cute, second, tall, blue, angry, brave, careful, healthy, little, old, generous, red, smart, two, small, tall, some, good, big, useful, interesting…
Example sentences:
An adverb modifies an adjective, verb, or another adverb. Many adverbs end in -ly, but not all do.
Examples:
Neatly, tomorrow, very, badly, fully, carefully, hardly, nearly, hungrily, never, quickly, silently, well, really, almost…
Example sentences:
Determiners and articles help clarify the nouns they introduce. Articles can be definite (the) or indefinite (a, an).
Examples:
The, a, an, this, that, these, those, many, few, each, every, some, any, no, which, what
Example sentences:
A conjunction connects words, phrases, or clauses. Some common conjunctions are and, but, or, so, because, and although.
Examples:
And, but, or, so, because, although, if, until, while, since, when, after, before, as
Example sentences:
A preposition shows the relationship of a noun (or pronoun) to another word. Common prepositions include at, on, in, by, with, and about.
Examples:
At, on, in, by, with, about, above, below, between, during, for, from, over, under, through
Example sentences:
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong emotion or sudden exclamation. Common interjections include wow, ouch, oh, and hey.
Examples:
Wow, ouch, oh, hey, ah, ugh, ew, hmm, yay, yikes, whoa, oops, aha, hurray, ew, oh no
Example sentences:
In this section, you’ve learned about different parts of speech with examples and sample sentences. Each part of speech plays a unique role in creating meaningful sentences.
To determine a part of speech in a sentence, look at the word being used, its context, and what meaning it brings to the sentence structure. Here are some questions you can ask about a particular word:
By asking these questions, you can identify the correct part of speech for any word in a sentence.
In its simplest form, a sentence can have one independent clause.
For example, the sentence “I walk to the store” contains one clause.
This entire sentence “I walk to the store” is an independent clause, expresses one subject doing one action — and is known as a simple sentence.
Knowing this, apply the fact that nouns and pronouns will often be the subjects or objects of simple sentences, while verbs will convey actions. So once again:
Complex sentences contain an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. These sentences use conjunctions such as because, since, which, or who to connect clauses. Consider the structure and an example below:
By combining these clauses, one forms a complex sentence: She reads a book because she wants to learn.
Other examples of complex sentences:
Learn all parts of speech in English with a useful video lesson.
Here are some Parts Of Speech exercises for you to practice:
A. In the sentence “I ran to the tallest tree”, what part of speech is the word “tallest”?
B. In the 2000s, the word staycation described the act of staying home for a vacation. Since “staycation” is a noun and a new word, what class of words does it belong to?
C. In the sentence “I’ll have a few tacos”, what part of speech is the phrase “a few”?
Answers: A) 3, B) 1, C) 3
An experienced English grammar teacher since 2015, with a dedication to helping students improve their language skills.
Latest posts by Grammargeek (see all)